Has the time come for a successor to ECMO?

Published April 2, 2024 11:01

Oxygen Increased Flow Advanced Membrane heralds a new era in the treatment of patients with severe cardiopulmonary failure. The project's developers hope that the successor to extracorporeal membrane blood oxygenation, ECMO, has just arrived. In the 6th Start-Up-Med Competition, which was a side event of the recently concluded 9th Health Challenges Congress in Katowice, the Silesian Medical University in Katowice won in the medical/scientific center category, having just presented the OXIFlame project.
What is ECMO?
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation) is a technique that involves oxygenating (oxygenating) the blood and eliminating carbon dioxide from it in an oxygenator, using extracorporeal circulation.
ECMO is used only in patients, in potentially reversible life-threatening conditions with very severe respiratory and/or circulatory failure, who have failed to respond to conventional treatments available in intensive care units.
ECMO does not cure the heart or lungs, but gives the patient a chance to survive the period when these organs are failing. It gives the doctor time to treat the disease that led to extreme cardiopulmonary failure.
There are two basic schemes for connecting veno-venous ECMO veno-venous (veno-venous VV ECMO) is used as respiratory support, while veno-arterial (veno - arterial VA ECMO) is used as cardiac and/or respiratory support.
VV ECMO is used in patients with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), in which the so-called alveolar-capillary barrier is damaged, causing protein-rich fluid to leak into the respiratory system. The collapse of the alveoli causes the lungs to lose their ability to perform their function of exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide, leading to hypoxia (anoxia). Among the causes of ARDS are a number of factors, including infectious and mechanical. The volume of one breath decreases dramatically. At this stage of therapy, the patient is intubated and mechanically ventilated, but as tidal volume decreases, the pressures generated can damage the lungs, and the use of a traditional ventilator becomes insufficient.
Extracorporeal oxygenation in this case reduces or eliminates the risk of lung injury associated with invasive mechanical ventilation in patients with severe ARDS.
VA ECMO used as cardiac support when the heart is failing in the course of a heart attack, cardiac arrest, pulmonary embolism or after major cardiac surgery. VA ECMO keeps a patient alive when his or her own heart is failing and avoids the cardiac damage associated with high doses of catecholamines, pressure-raising drugs, while maintaining tissue perfusion (blood supply to tissues).
Advantages and disadvantages of ECMO
However, it should be emphasized that ECMO is a highly invasive therapy, so it should only be used when stabilization of the patient cannot be achieved with conventional methods - such as mechanical ventilation or the use of pressure-raising drugs - and the life-threatening condition is potentially reversible.
Hence, the right qualification is very important: the right patient at the right time, with reversible disease.
A bit of history...
The first successful human cardiopulmonary bypass was performed by John H. Gibbon, Jr. in 1953, but it wasn't until 1971 that the prototype ECMO was used to assist a trauma patient. The patient survived for three days, with the device taking up an entire room, but he is considered the first patient to benefit from the technology. A few years later, in 1975, Robert H. Bartlett reported the first infant to be saved by ECMO.
Since then, research has been ongoing to improve the device. Coating the inside of the cannulas, drains and the oxygenator itself with heparin and albumin has made it possible to reduce the intensity of anticoagulation required (from four times the clotting time to one and a half times this standard). This made it possible to prolong the work of ECMO, its size was reduced, and it now consists of: ECMO oxygenator (diffusion membrane), centrifugal pump, cannulas, set of drains and heat exchanger (heater).
Despite such advanced technology and numerous modifications to its functioning, the results of treating patients who require ECMO are still far from optimal because only 30-58% of qualified patients can be disconnected from the device, and even fewer of them survive the hospitalization period. The post-treatment rehabilitation period takes a long time and often does not allow patients to return to their full strength from before the disease.
It's time for OXIFlame!
Faced with numerous problems with the device, a meeting of experts from three different fields took place: recognized ECMO expert Ewa Trejnowska, MD, from the Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care (Silesian Center for Heart Diseases in Zabrze, Faculty of Medical Sciences in Zabrze, Silesian Medical University in Katowice) , Szymon Skoczyński, M.D., Ph.D., Professor of SUM from the Department of Pulmonary and Tuberculosis Diseases of SUM ( Faculty of Medical Sciences in Zabrze, Silesian Medical University in Katowice, specialist in respiratory diseases and respiratory pathophysiology), and Andrzej Swinarew, M.D., Professor of SUM. (biomaterials specialist Institute of Biomedical Engineering, University of Silesia Katowice, Institute of Sport Science, Academy of Physical Education in Katowice). At the stage of further work, the initiating team was supported by scientists and clinicians representing all three universities: Jadwiga Gabor, Hubert Okła, Mateusz Przybyła, Grzegorz Brożek, Agnieszka Skoczyńska, Piotr Knapik, Tomasz Darocha, Konrad Mendrala, Katarzyna Mizia-Stec, Arkadiusz Stanula, Barbara Szpikowska-Sroka, Magdalena Popczyk.
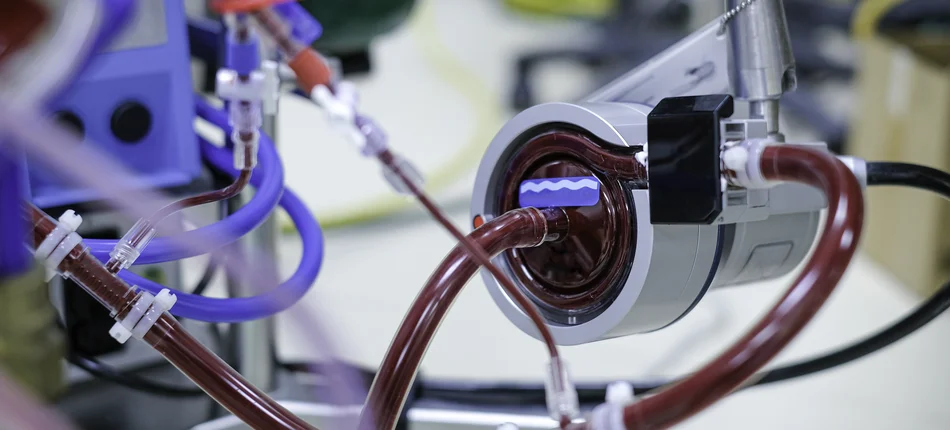
The work carried out resulted in the development of OXiFlame, a completely new concept for the construction of an oxygenator, which allows the device's operation to function under oxygenation conditions much closer to the physiological ones observed in nature. The team created the design of the device, which is built from completely different materials than before. The materials created from scratch are characterized by a smooth surface, reducing the likelihood of thrombus formation; in addition, the porous material is filled with anticoagulant particles. Such innovation makes the created material "alive", just like the wall of a blood vessel and subject to interaction with the flowing blood. The anticoagulant molecules that are sheared off the device's surface by the flowing blood during operation are replaced by new ones that diffuse (flow) to the surface from within the material, protecting it from clotting. This phenomenon, along with the functioning of the device, improves permeability to gases, which currently, in the currently functioning ECMO, deteriorates with time of use. The up-initio materials tested also allow the use of much lower oxygen concentrations than in currently functioning devices. With this innovation, it will be possible to reduce the oxidative stress observed in currently functioning ECMO, which intensifies vascular endothelial activation, activates the coagulation system and contributes to the activation of leukocytes their migration and generalized inflammatory response. These phenomena are responsible for the complications currently observed during ECMO therapy, such as bleeding, caused, among other things, by the activation of the coagulation system in the currently used oxygenatorzel or clotting in the case of insufficient supply of anticoagulant threaten arterial embolisms, among other strokes. Other common complications of oxidative stress are infections, sepsis and septic shock. This creates the need for frequent replacement of the currently functioning oxygenator in ECMO (recommended by manufacturers 14 days).
The material used in OXiFLAME, thanks to the proposed concept, avoids these drawbacks. The next stage of the initiative during the development of OXiFLAME was the creation of a completely new oxygenator, operating on the principle of a physiological countercurrent, taken from the normal histological structure of the lung or kidney. This allows a significant reduction in oxygen supply to concentrations lower than 50% of the respiratory mixture composition. As a result, it is possible to significantly reduce the stress on the oxygenator, reduce the likelihood of complications and, in the process, extend the life of the device. The structure of the oxygenator and the use of a double circuit of flows through filters created from the same material allow the removal of thrombi from the system without replacing the oxygenator (currently, this is technically problematic and can pose a risk to the patient). Any micro thrombi will not find their way into the mainstream blood stream because the vortex motion, will allow them to be effectively displaced.
The future of OXIFlame
OXiFlame was first presented at the ELSO-ECMO conference in Boston in 2022, where it was recognized as the most interesting convention report. The solution is protected by numerous Polish patents. It has also been filed with patent offices within the European Union and the United States of America. - For rapid implementation and testing in laboratory and clinical conditions, cooperation with the biomedical industry is necessary, which we are open to," explains Prof. Skoczynski.
Source: Silesian Medical University